The majority of photographs of nebula are in a false color palette. False-color photographs of nebulae are essentially color (RGB) photographs whose color channels have been mapped to specific emission lines. In these images, each color can represent a specific element. In other words, a false-color image of a nebula tells us exactly what it’s made of. There are many emission lines, but the three most photographed by astronomers are hydrogen-alpha, oxygen-III and sulfur-II. These emission lines are captured by using narrowband filters which only let through the light at very specific wavelengths, typically most of my photographs are taken with filters allowing a bandwidth of 3µm.
|
Element
|
Emission line
|
Wavelength
|
Color
|
|
Hydrogen
|
Hα
|
656.3 nm
|
Red
|
|
Oxygen
|
O-III
|
500.7 nm
|
Blue/Green
|
|
Sulfur
|
S-II
|
672.4 nm
|
Red
|
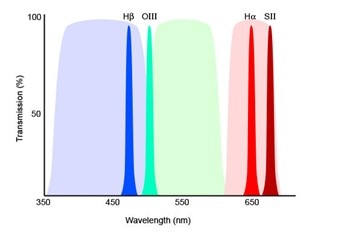
Mapping Hα, O-III and S-II to red, green and blue is problematic when two of them are red, one is blue/green, and none is pure blue. Astronomers deal with this by using false color — one or more of these elements will have to take a hit for the team and take on an unnatural hue. The HOO color palette assigns red to Hα, green and blue to O-III: red is accurate, and green and blue are false. Sometimes, some astrophotogers add some Hα to the O-III in the green channel for a synthetic green. The point of this color palette is to emphasize specific nebula structures so that they are more prominent. This photograph uses the HOO color palette, hence the reds and blues you find in the photograph.